7th Funky Function:
A continuous, non-constant, differentiable function
whose derivative is zero everywhere
except on a set of Lebesgue measure zero.
| > |
The Maple Code on this page is from I.N. Galidakis
(http://ioannis.virtualcomposer2000.com/math/cantor.html).
Special thanks to him!
| > |
It's the Cantor Function f: [0,1] -> [0,1].
As explained at the Wiki link,
the Cantor function is the uniform limit
of a sequence {![]() } of piecewise linear functions.
} of piecewise linear functions.
Let's graph
f_0, f_1, f_2, .... f_enough ,
each on it's own grid.
So we will have (enough+1) graphs.
| > |
| > | restart; with(plots):
enough := 3; CF:=proc(a,b,c,d,n,x) option remember; if n=0 then solve((d-c)/(b-a)=(y-c)/(x-a),y); else #n>0 piecewise(a<=x and x<=a+1/3*abs(a-b),CF(a,a+1/3*abs(a-b),c,c+1/2*abs(c-d),n-1,x), b-1/3*abs(a-b)<=x and x<=b, CF(b-1/3*abs(a-b),b,d-1/2*abs(c-d),d,n-1,x), c+1/2*abs(c-d)); fi; end: for n from 0 to enough do plot(CF(0,1,0,1,n,x),x=0..1,numpoints=300); od; |
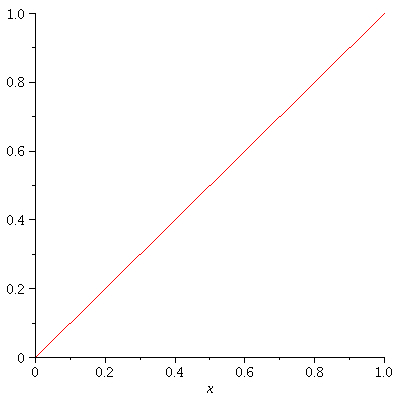 |
|
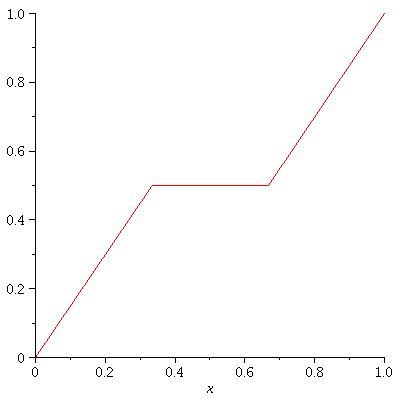 |
|
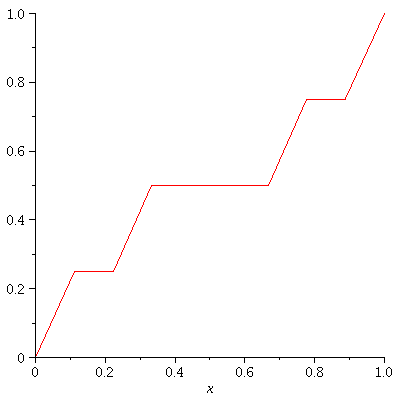 |
|
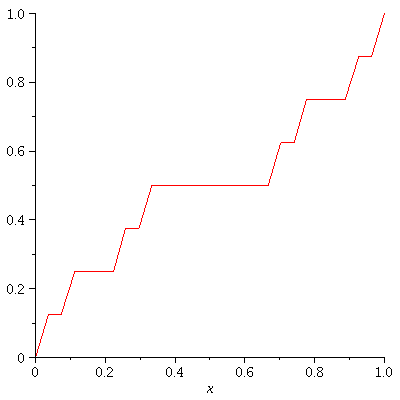 |
| > |
Next let's graph
f_0, f_1, f_2, .... f_enough
all on the same grid in a fancy
"animated" effect with the f_n's
forming a "moving picture". I set
the speed at 1 frame per second
so it will take (enough+1) seconds to show
you f_0 through f_enough
| > |
| > | restart; with(plots):
enough := 9; CF:=proc(a,b,c,d,n,x) option remember; if n=0 then solve((d-c)/(b-a)=(y-c)/(x-a),y); else #n>0 piecewise(a<=x and x<=a+1/3*abs(a-b),CF(a,a+1/3*abs(a-b),c,c+1/2*abs(c-d),n-1,x), b-1/3*abs(a-b)<=x and x<=b, CF(b-1/3*abs(a-b),b,d-1/2*abs(c-d),d,n-1,x), c+1/2*abs(c-d)); fi; end: q1:=[seq(CF(0,1,0,1,n,x), n=0..enough)]: q2:=[seq(plot(g,x=0..1),g=q1)]: display(q2,insequence=true); |
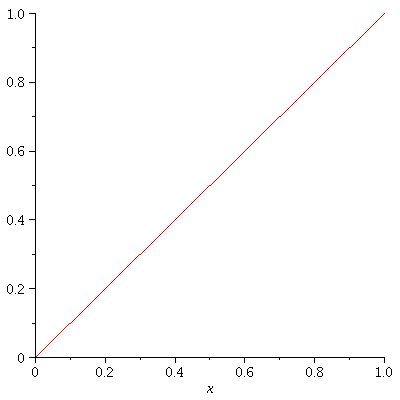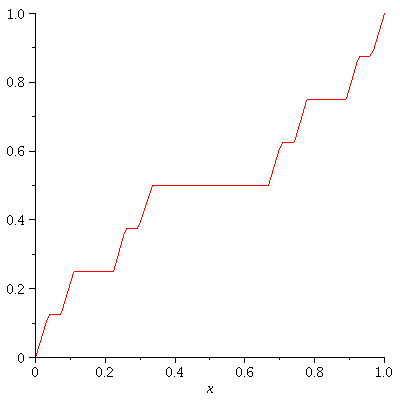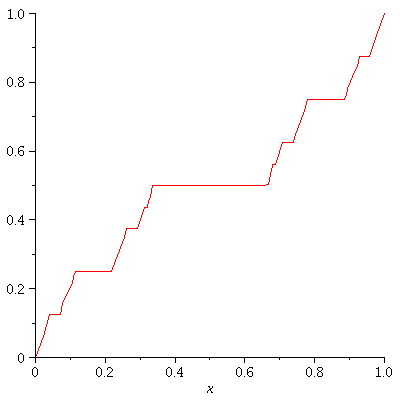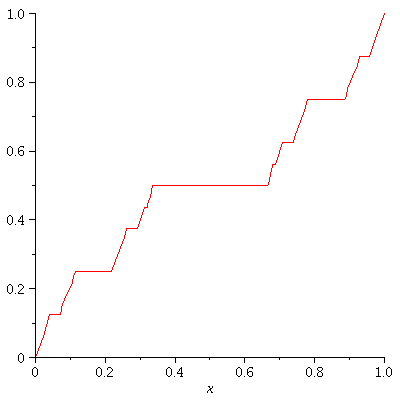 |
| > |
| > |
That's all!